|
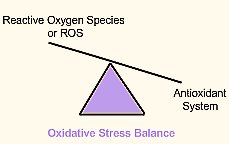
Oxidative Stress is the root
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RADICAL ROS | Non-RADICAL ROS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl | OH- | Peroxynitrite | ONOO- |
| Superoxide | O2- | Hypochloric acid | HOCl |
| Nitric Oxide | NO | Hydrogen Peroxide | H2O2 |
| Thyl | RS | Singlet Oxygen | 102 |
| Peroxyl | RO2 | Ozone | O3 |
| Lipid Peroxyl | LOO | Lipid peroxide | LOOH |
Effects of oxidative stress to a cell vary from cell damage, apoptosis or cell suicide, and necrosis.
Some body organs are predisposed to greater levels of ROS than others. These are the lungs, brain, eye, heart and reproductive organs.
The lungs are exposed to high levels of high ROS because it is exposed to continuous high levels of oxygen.
The brain, on the other hand, is susceptible to oxidative stress since it involves high metabolic activity. The brain is, after all, the body's main control mechanism. Moreover, the brain has low levels of endogenous antioxidants to counteract ROS.
The eye is predisposed to formation of ROS because it is constantly exposed to damaging UV light.
Cataract is an example of an eye inflammation whose one possible cause in too much ROS.
The heart, just like the lungs, is exposed to high levels of oxygen. And it involves a lot of energy since it is the body's main lifeblood.
The reproductive organs, both male and female, have also been found to produce ROS. In females, ROS have been found in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and embryos. As such, some evidence shows it has a role in endometriosis and unexplained infertility.1
ROS have been implicated in oxidative stress-induced male infertility as well as female infertility
Free radicals or ROS can damage the membranes of the sperm cell, affecting sperm motility. It can also damage the DNA that may be passed to the woman's egg cell in conception.
Oxidative stress in female infertility has been observed in various reproductive processes.
For couples who want to have a baby, a "damaged" sperm cell is definitely not welcome!
Back to top
Role in Diseases
The effects of oxidative stress have been implicated in a growing list of diseases as well as the aging process.
Some of these diseases include the following:
- Cardiovascular
- Inflammatory
- Metabolic Disorders
- Diseases of the central nervous system
- Male Infertility
- Female Infertility
- Chronic Fatige Syndrome
The Role of glutathione in fighting cellular inflammation is evidenced by some incredible Glutathione Testimonials.
The use of antioxidants to prevent and/or cure diseases remains controversial. However, several studies and researches have shown that stress caused by ROS is one of the major causes of the above-mentioned diseases. Antioxidant supplementation may, therefore, be of help in managing and treating these diseases.
The body has its own antioxidant system to fight ROS. This system includes antioxidants and antioxidant enzymes.
Endogenous antioxidants are the following: Glutathione,the body's master antioxidant, Coenzyme Q10 and Alpha Lipoic Acid.
The body's own antioxidant enzymes include catalase, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase.
Apart from the body's own antioxidant system, it also needs exogenous (consumed) antioxidants such as Vit. C and A.
Antioxidants can be classified according to their function. They can either be scavenging or preventing.
A. Scavenging antioxidants seek out for ROS and remove them. Examples of scavenging antioxidants are the water-soluble Vit. C and glutathione. Some are lipid-soluble. Vit. E, carotenoids, lipoic acid and coenzyme Q10 belong to this group.
Scavenging antioxidant enzymes include superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx).
SOD detoxifies the superoxide ion (O2-). Catalase deals with the hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) radical. Glutathione peroxidase detoxifies cellular peroxides.
B. Preventive antioxidants, on the other hand, prevent ROS formation. They are proteins that bind with ROS to protect essential proteins.
Preventive antioxidants include albumin, metallothionein, transferrin, ceruloplasmin, myglobin and ferritin.
Read on glutathione-antioxidant FAQ's here.
In summary, oxidative stress occurs when our body's own antioxidant system cannot cope with the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
ROS form when our body is attacked by too much free radicals which can come from normal biological functions and from outside stressors.
Outside stressors include automobile exhaust, UV rays, cigarette smoking, to cite the most common.
So how do we avoid oxidative stress?
We should avoid the things that cause free radical formation such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Avoiding places and people that stress us out will definitely keep us "stress-free."
Regular exercise also helps by boosting your immune system. And it makes you feel happy afterwards.

In terms of food and supplements, it is wise to eat foods rich in antioxidants. The same goes for antioxidant supplements, particularly supplements that increase our glutathione reserves.
Be sure to take in a variety of antioxidants in order to get the most of all their benefits. Boost your own body's master antioxidant, glutathione. And also, take in exogenous antioxidants such as Vit. C and Vit. E.
So, if you want to live (healthy) longer and be free of diseases, then take protect your cells form ROS!
Your body will be at its healthiest.
And if you're healthy, you can do more things that you enjoy, longer! Isn't that what we all want?
REFERENCES:
1Ashok Agarwal, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress in Female Reproduction. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 2005. July 30,2009. http://www.rbej.com/content/3/1/28
Oxidative Stress and Nitrostative Stress Overview. Retrieved July 30,2009, from Oxis International website
Oxidative stress. Retrived July 27,2009, from Wikipedia
Read my
Return from Oxidative Stress to HOME